software robots
Software robots are efficient virtual employees who perform complex routine work in large volumes, quickly and without errors.
The robot does not need weekends, vacations, breaks. The robot does not get sick or late, does not require an office space or paying taxes.
robots can be and have to be used
It is possible and necessary to robotize any business processes that are repeated many times under a strict algorithm. These processes are traditionally performed by a human, but do not require an intelligent solution.
If such an intelligent solution is required, the robot makes a preparation step, asks a human to make a decision and then continues and completely finishes the work process.
application efficiency
The use of software robots is cost-effective even for one-time but very complex tasks, such as transferring large amounts of data from one system to another.
The high speed and accuracy saves significant human resources in solving such tasks.benefits for the company
up to 60%
costs reduction
less than 1%
5-100x
faster execution
24/7
works around the clock
55% lower
implementation cost
compared to classic automation
3-5 x faster
implementation
compared to classic automation
benefits for employees
A Forrester Consulting study commissioned by UiPath confirmed that humans must be at the center of RPA implementation efforts. The research recommends that companies aim to simultaneously improve operational efficiency and create positive perceptions among employees. Both are possible through creating RPA centers of excellence, managing psychological issues during implementation and using human-centered change management processes that take into account the human factor and make people feel valued and safe.
60% more focus
on strategic tasks
57% fewer
manual errors
86% higher
efficiency
57% higher involvement
of employees
67% deeper understanding
of clients
57% better
client service
application areas
CAPABILITIES of RPA
The basic logic of software robots is based on the imitation of human actions. The robot also needs a computer (local, remote, virtual machine) to function.
The robot operates the same applications and file system performing a predetermined sequence of actions of any complexity. Instantly, developer’s logic is processed - execution of branching scenarios depending on the progress of the process.
types of robots
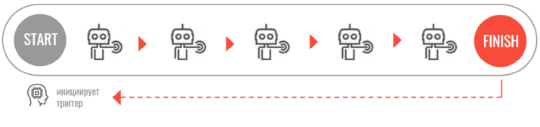
autonomous robots UNATTENDED
Autonomous robots are effective digital employees. They begin to work by a trigger (time, email or file). The robots can be activated by other robots, completely go through the algorithm and start a new iteration or wait for the next trigger.
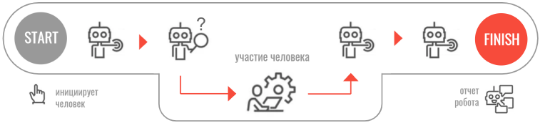
robots-assistants ATTENDED
Robots-assistants are digital helpers, speeding up and facilitating tasks. Launched by humans, they perform a part of a process, interact with humans, wait for a decision to be made, then continue their work and report back on the results.
ALGORITHM for creating software robots
preparation stage
consultation, first meeting with the client
getting to know each other, discussing problems and challenges
PREPARATION STAGE
exploratory design
- search, analysis and evaluation of processes suitable for robotic automation
- interviewing of process participants, collection of information
- recommendations for process optimization
production
design and development of robots
development, scripting
final
outcome evaluation and implementation
testing, working out reactions to algorithm interference
support
WARRANTY AND AFTERSALES SERVICE
warranty, technical support, adjustments to process changes
how to find and choose a process for robotic automation?
Robots can be small, solving little specific tasks, or rather large and powerful, processing long and complex processes, with calls to subprograms and modules, with possible branching of subtasks, processing of various conditions, etc.
Robots can be run manually, scheduled, triggered (by an event), or even run 24 hours a day, processing large amounts of data or waiting for new ones to appear.
There are two main approaches to finding tasks for robotic automation:
evaluation criteria of processes
When selecting processes for robotic automation, the company's existing and planned business processes (both with and without human involvement) are analyzed according to the following evaluation criteria:
- algorithmizable
- stable
- labor-intensive
- financially expensive
- performed regularly and/or take a long time
- require improvement
- collect data from multiple systems
- transfer data from one system to another
- validate data in multiple systems
- enter data into multiple systems
EXAMPLE OF CALCULATING COST-EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING A ROBOT - ROI
Here is an example of calculating ROI for robotic automation that frees up the resources of three employees to perform other tasks.
Number of employees involved in the process: 3
Average annual payroll per employee: 900K ₽ (75K ₽/month)
The process takes 50% of an employee's time.
current cost
of the process
1 year - 1.35M ₽
3 years - 4.05M ₽
5 years - 6.75M ₽
process cost
with automation
1 year - 295K ₽
3 years - 384K ₽
5 years - 472K ₽
estimated
ROI
In a year - 457%
In three years - 1,054%
In five years - 1,430%






 .
.